时间片轮转调度算法模拟
1. 实验目的
了解时间片轮转调度算法的工作原理,通过编写调度算法的程序,加深对Linux进程时间片调度的理解。
2. 实验内容
在Linux上编写C语言,实现从键盘输入时间片长度、任务个数、每一个任务的到达时间及服务时间;
构造相应的进程并按时间片轮转调度算法对所有进程进行调度,进程运行情况可以输出到终端,从而深入理解时间片轮转调度算法的原理。
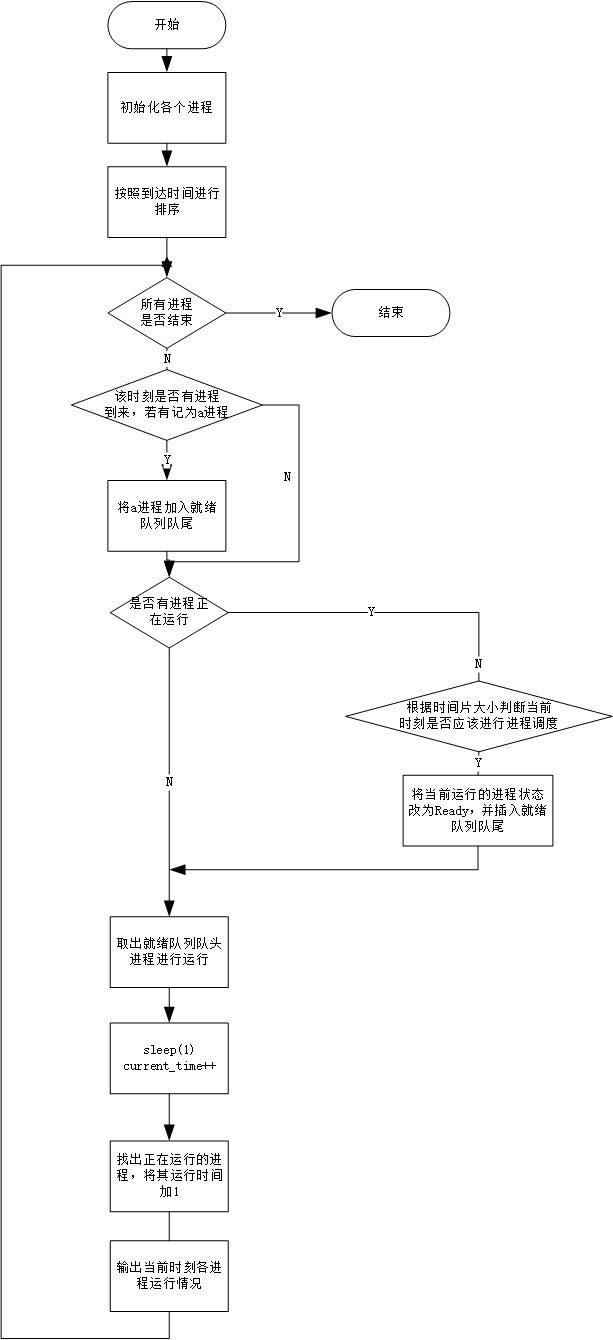
2.1 程序流程图
程序中就绪队列用int型的数组表示,并用readyIndex表示下一个要插入就绪队列的位置,该数组中存放进程数组的下标,方便进程调度时进行使用。
程序中进程状态用枚举类型表示如下,其中NOT_COME表示进程还未到来,READY表示进程在就绪队列中等待,RUNNING及FINISH表示正在运行和运行结束。程序中进程块PCB结构体如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
typedef enum PROCESS_STATE{
NOT_COME,
READY,
RUNNING,
FINISH
} PROCESS_STATE;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
typedef struct{
char process_name[10];
int arrive_time;
int service_time;
int start_time;
int end_time; //已经运行的时间
int cpu_time;
PROCESS_STATE state;
} PCB;
- 程序流程图如下:
2.2 程序源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <malloc.h>
typedef enum PROCESS_STATE
{
NOT_COME,
READY,
RUNNING,
FINISH
} PROCESS_STATE;
typedef struct
{
char process_name[10];
int arrive_time;
int service_time;
int start_time;
int end_time;
//已经运行的时间
int cpu_time;
PROCESS_STATE state;
} PCB;
int processs_num;
PCB *process_list;
int *ready_list;
int readyIndex = 0;
int current_time = 0;
//时间片大小
int quantum;
void SortList();
void InitList();
//判断所有进程是否运行结束
int isEnd();
//判断当前时间是否有进程到达,若有但返回index,反之返回0
int isProcessArrive();
int isProcessEnd(int index);
void MoveReadyList();
void showState();
int haveRunningProcess();
int main() {
printf("进程个数:");
scanf("%d", &processs_num);
process_list = (PCB *)malloc(sizeof(PCB) * (processs_num + 1));
ready_list = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (processs_num + 1));
printf("时间片长度:(>=1):");
scanf("%d", &quantum);
//初始化进程列表,并按到达时间排序
InitList();
printf("进程名称\t到达时间\t服务时间:\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= processs_num; i++) {
printf("%s\t\t%d\t\t%d\n", process_list[i].process_name,
process_list[i].arrive_time, process_list[i].service_time);
}
while(!isEnd()){
int runningIndex;
int index = isProcessArrive();
//有进程到来
if(index != 0){
ready_list[readyIndex] = index;
process_list[index].state = READY;
readyIndex++;
}
runningIndex = haveRunningProcess();
PCB temp = process_list[runningIndex];
//有正在运行的进程
if(runningIndex != 0){
//判断是否应该进行进程调度(根据时间片)
if((temp.start_time + temp.cpu_time) % quantum == 0){
process_list[runningIndex].state = READY;
ready_list[readyIndex] = runningIndex;
readyIndex++;
}
}
//取出就绪队列队头进行运行
//printf("index %d\n",readyIndex);
if(readyIndex > 0 && (temp.start_time + temp.cpu_time) % quantum == 0){
int num = ready_list[0];
process_list[num].state = RUNNING;
if(process_list[num].start_time == -1)
process_list[num].start_time = current_time;
//就读队列向前移动一位
MoveReadyList();
}
//延时1s
sleep(1);
current_time++;
//重新获取当前正在运行的进程
runningIndex = haveRunningProcess();
process_list[runningIndex].cpu_time++;
if(isProcessEnd(runningIndex)){
process_list[runningIndex].state = FINISH;
process_list[runningIndex].end_time = current_time;
}
printf("%d~%d运行的进程为:%s\n", current_time-1, current_time, process_list[runningIndex].process_name);
printf("%d时刻:\n", current_time);
showState();
}
return 0;
}
void InitList(){
printf("输入进程名称,到达时间以及服务时间:\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= processs_num; i++) {
scanf("%s %d %d", process_list[i].process_name,
&process_list[i].arrive_time, &process_list[i].service_time);
process_list[i].cpu_time = 0;
process_list[i].state = NOT_COME;
process_list[i].start_time = -1;
process_list[i].end_time = -1;
process_list[i].cpu_time = 0;
}
//按照到达时间排序
SortList();
}
void SortList(){
for(int i = 1; i< processs_num; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < processs_num - i + 1; j++){
if(process_list[j].arrive_time > process_list[j+1].arrive_time){
PCB temp = process_list[j];
process_list[j] = process_list[j+1];
process_list[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int isEnd(){
for(int i = 1; i <= processs_num; i++){
if(process_list[i].state != FINISH)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int isProcessArrive(){
for(int i = 1; i <= processs_num; i++){
if(process_list[i].arrive_time == current_time)
return i;
}
return 0;
}
int haveRunningProcess(){
for(int i = 1; i <= processs_num; i++){
if(process_list[i].state == RUNNING)
return i;
}
return 0;
}
int isProcessEnd(int index){
if(process_list[index].cpu_time == process_list[index].service_time){
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
void MoveReadyList(){
for(int i = 0; i < readyIndex - 1; i++){
ready_list[i] = ready_list[i+1];
}
readyIndex--;
}
void showState(){
printf("进程名称\t开始时间\t结束时间\t运行时间\t到达时间\t服务时间\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= processs_num; i++) {
printf("%s\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t", process_list[i].process_name,
process_list[i].start_time, process_list[i].end_time, process_list[i].cpu_time,
process_list[i].arrive_time, process_list[i].service_time);
switch (process_list[i].state)
{
case NOT_COME:
printf("not come");
break;
case READY:
printf("ready");
break;
case RUNNING:
printf("running");
break;
case FINISH:
printf("finish");
break;
default:
break;
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
运行测试如下: 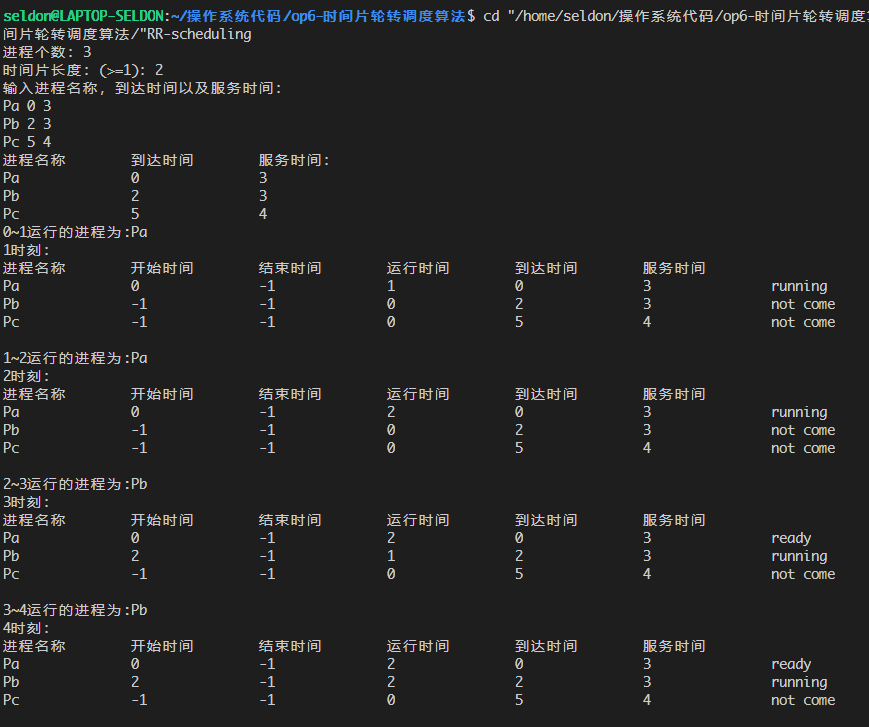
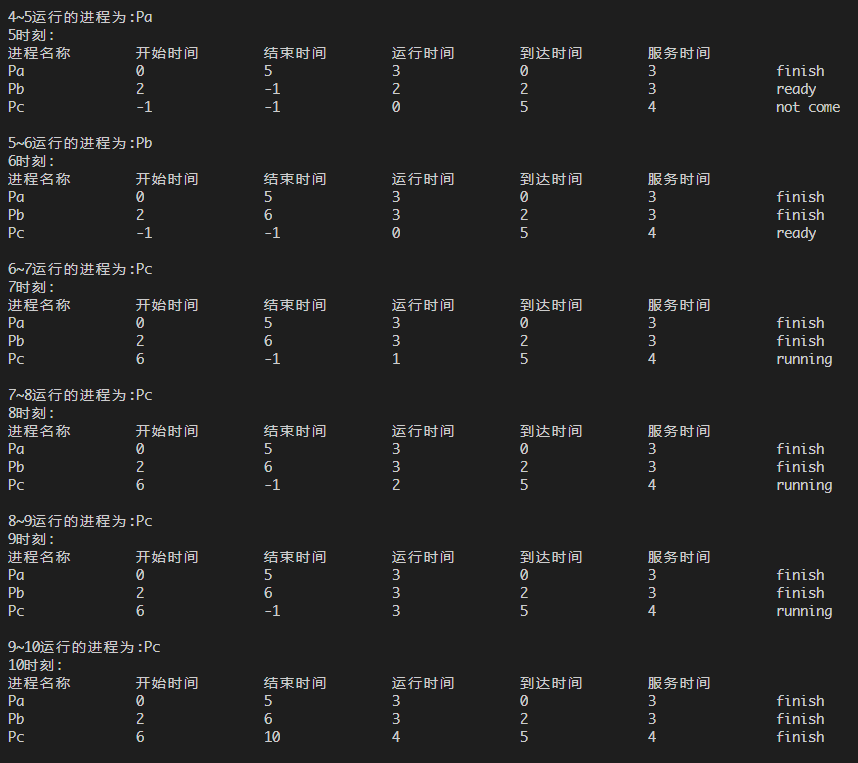
经逐步验证,程序结果无误。
3. 实验总结
通过编写程序模拟时间片轮转调度算法
- 深入了解了无优先级时进程调度的原理
- 对操作系统如何实现多进程调度有了进一步的理解